e@syFile error: (" The value of source code (4587) 'xxxxxxx' cannot exceed the lower of R1.25 mil or the total of the values declared under foreign service income codes 'xxxxxx') when source code 4587 exceeds R1.25 mil
Summary
Description
Code 4587 is only valid from 2021 year of assessment and is an information code which reports the section 10(1)(o)(i) foreign employment income exemption taken into account by the employer for PAYE purposes on the tax certificate. If the employee received foreign employment income but did not qualify for the exemption in terms of section 10(1)(o)(ii) of the Income Tax Act, then code 4587 will be zero. The exemption limit is R1.25 million per tax year, therefore, code 4587 cannot exceed this value.
Rules for information code 4587:
- If no foreign service income codes are completed, then code 4587 must not be completed.
- If any of the foreign service income codes allowable for the s10(1)(o)(ii) exemption is completed, then code 4587 must be completed.
- The value of source code 4587 cannot exceed the lower of R 1.25 million (the exemption limit) or the total of the values declared under the s10(1)(o)(ii) allowable foreign service income codes.
The following foreign service income source codes are included in the remuneration which qualifies for the s10(1)(o)(ii) exemption and which employers may consider for calculating PAYE, if all requirements are met:
- Income Source codes – 3651,3655,3656,3657
- Allowance codes – 3751,3763,3767,3768,3772
- Fringe Benefit codes- 3851,3852,3855,3856,3858,3859,3860,3863,3866,3867,3870,3875,3878,3879,3881,3883
Read more in the SARS Business Requirement Specification (BRS) 2020 release.
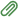 NOTE: The total value for source code 4587 may not exceed R1.25 mil
NOTE: The total value for source code 4587 may not exceed R1.25 mil
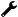 EXAMPLE: Employees IRP5 tax certificate from the payroll system that exceeds R1.25 million
EXAMPLE: Employees IRP5 tax certificate from the payroll system that exceeds R1.25 million

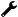 EXAMPLE: e@syFile error
EXAMPLE: e@syFile error

Resolution
The exemption limit per tax year is R1.25 million, since the foreign employment income values reported on this record exceed R1.25 million, the payslip values need to be adjusted and corrections must be made.
 NOTE: The system will not apply the exemption automatically due to numerous variables to be considered by employers, for example the qualifying periods, employment at more than one employer during the tax year, amounts paid/benefits received by foreign employer etc. It is the user’s responsibility to apply the foreign employment exemption on the payroll and report against the relevant IRP5 code.
NOTE: The system will not apply the exemption automatically due to numerous variables to be considered by employers, for example the qualifying periods, employment at more than one employer during the tax year, amounts paid/benefits received by foreign employer etc. It is the user’s responsibility to apply the foreign employment exemption on the payroll and report against the relevant IRP5 code.
The following steps must be followed on the payroll to correct the employees tax record:
 NOTE: Refer to Release Notes 5.4a for more information. From the Company Listing screen, click on Release Notes, select View Full Release notes on 54a
NOTE: Refer to Release Notes 5.4a for more information. From the Company Listing screen, click on Release Notes, select View Full Release notes on 54a
Step 1:
If the employee is working outside RSA for or on behalf of the employer, determine whether the employee qualifies for the foreign employment income exemption according to the days rules (i.e. outside South Africa for a period (or periods) exceeding 183 full days in any 12 months and for a continuous period exceeding 60 full days in total in that period of 12 months), if yes continue to step 2.
If no, remuneration for services rendered outside RSA for or on behalf of the employer is still loaded on an employee record flagged for foreign income (to ensure it is reported on foreign employment income IRP5 codes), but with a normal taxable tax status (for example Statutory Tables) and the remuneration is subject to PAYE, UIF (unless a specific UIF exemption reason is applicable, for example Temporary) and SDL.
Step 2:
Determine if the remuneration received for services rendered outside RSA for or on behalf of the employer is within the exemption limit. If yes, continue to step 3.
If the foreign employment income exceeds the exemption limit, continue to step 4.
Step 3:
This exempt foreign employment income is loaded on an employee record flagged for foreign income (to ensure it is reported on foreign employment income IRP5 codes), and with a tax status set to No Tax. The remuneration is not subject to PAYE, UIF and SDL.
Step 4:
As soon as the exemption limit is exceeded, the remuneration should be subject to PAYE, UIF and SDL. This remuneration is still loaded on a record flagged for foreign income (to ensure it is reported on foreign employment income IRP5 codes), but with a normal taxable tax status (for example Statutory Tables) and the remuneration is subject to PAYE, UIF (unless a specific UIF exemption reason is applicable, for example Temporary) and SDL.
- Terminate the exempt foreign employment income record referred to in step 3.
- Create a new record with a new IRP5 start date. Click here for the options on how to create an employee's record
- Select the relevant tax status to calculate PAYE (for example Statutory Tables).
- UIF and SDL should calculate for this record (unless a specific UIF exemption reason is applicable, for example Temporary).
- Routing entry field: Type FI. A message will display asking whether you want to Flag this employee for Foreign Income, select <Yes>. FI will display in brackets next to the Tax Status label.
- The foreign employment income exceeding the exemption limit should be processed on this record.
 NOTE: If the limit is reached in the middle of the month, income must be split between the exempt and taxable records (refer to step 3 and 4 above). If the employee returns to RSA to perform services in RSA for or on behalf of the employer, the remuneration should be processed on a new record with normal IRP5 codes (not flagged for foreign income) and must be subject to PAYE, UIF and SDL.
NOTE: If the limit is reached in the middle of the month, income must be split between the exempt and taxable records (refer to step 3 and 4 above). If the employee returns to RSA to perform services in RSA for or on behalf of the employer, the remuneration should be processed on a new record with normal IRP5 codes (not flagged for foreign income) and must be subject to PAYE, UIF and SDL.
- Click here for steps on how to make changes to History screen
 NOTE: If you require any further assistance, kindly contact your Accountant, Tax Practioner, or Accredited Business Partner
NOTE: If you require any further assistance, kindly contact your Accountant, Tax Practioner, or Accredited Business Partner
Solution Properties
- Solution ID
- 210508122934210
- Last Modified Date
- Tue May 02 12:42:39 UTC 2023
- Views
- 0